When choosing binoculars or spotting scopes, you’ll notice different glass types mentioned. Which glass is better for image quality?

BaK-4 offers a brighter and rounded image compared to BK-7 but is more expensive of the two. The K-9 type is equivalent to BK-7.
Prism Glass Types
You’ll find different types of prism glass in binoculars, spotting scopes, and monoculars.
What is a prism? In terms of binoculars and scopes, a prism is a glass component inside the instrument that corrects the image to the right way up (I wrote about the upside down image effect elsewhere).
In such a context, there are two types of prisms: roof and porro…
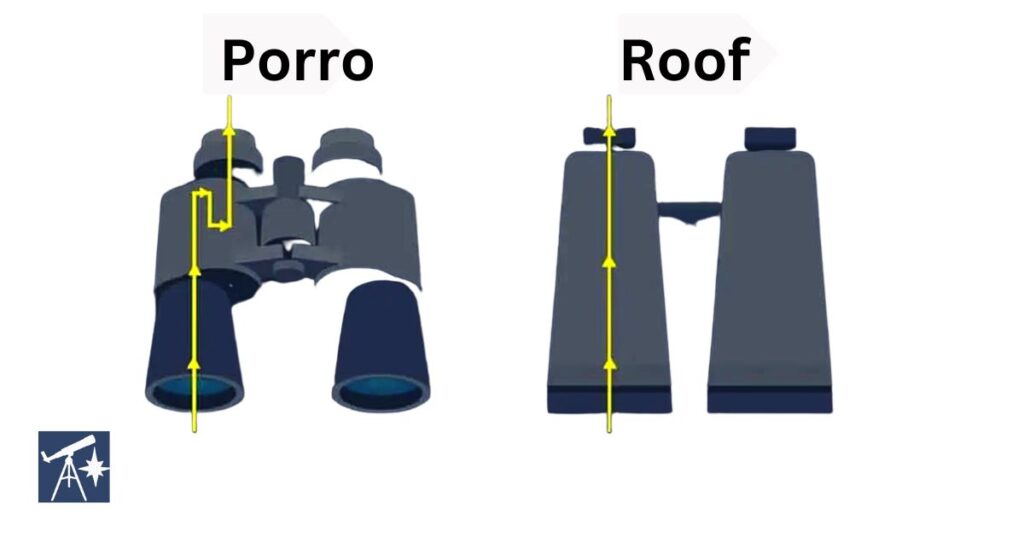
When I was looking for gear as a newbie I had no idea what the different glass types meant or what they referred to when reading the specifications.
Like me, you’ll come across the following describing the optics:
- BK-7
- K-9
- BaK-4
Celestron briefly explains the difference between these glass types.
But here’s more on what I discovered about these prism glass types…
BK-7
B = boron. K= Krone (German for Crown).
- Borosilicate crown glass
- Less expensive
- Moderate refractive index, nd (1.517)
- Lower dispersion*, vd (64.20)
- Exit pupil with blurred edges
- Manufactured by Schott
*Dispersion describes the variation of the refractive index with wavelength. Lower Vd numbers, in the range 90–20, correspond to higher dispersion.
K-9
K= Krone (German for Crown). 9 = 9% lead oxide content.
- Borosilicate crown glass
- Less expensive
- Manufactured in China
- Equivalent to BK7
- Also known as K9 crystal
BaK-4
Ba = barium. K= Krone (German for Crown).
- A light barium crown glass
- More expensive
- Higher refractive index, nd (1.569)
- Dispersion, vd (56.10)
- Higher levels of image quality
- Image tends to be superbly round (round exit pupil)
- Used for prisms in high-end binoculars
Borosilicate crown glass vs barium crown glass
Crown glass is used in optical components such as lenses and prisms.
Borosilicate glass is manufactured from alkali-lime silicates with about 10% boric oxide (B2O3). First developed by Otto Schott, a German glassmaker in the late 19th century.
Barium crown glass is borosilicate glass with the addition of barium, zinc, potassium, and sodium.
Best choice
Of the three above, binoculars with BaK-4 are considered the best choice. The higher refractive index offers brighter images — plus there’s no interference in the exit pupil, whereas the BK-7 distorts around the periphery — see diagram… (Thanks to Microglobe).
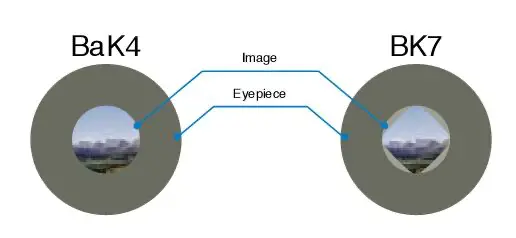
You do pay more for the quality. It’s a trade-off between better views and cost.
Cheaper binoculars tend to have Bk7 prisms.
By the way… plastic lenses offer low cost but inferior performance compared to glass lenses. They are susceptible to warping and less durable.
Ideally you’ll opt for the best optical glass for clarity at high magnification with reduced chromatic aberration (color distortion) for your experience when exploring the night sky with binoculars.
